Creating Idea route in Rails
In the previous page, we have created our first three ideas while playing around with Rails console].
In this page, we will setup the required route in our application which will help us to display those ideas in the browser.
Request and response flow
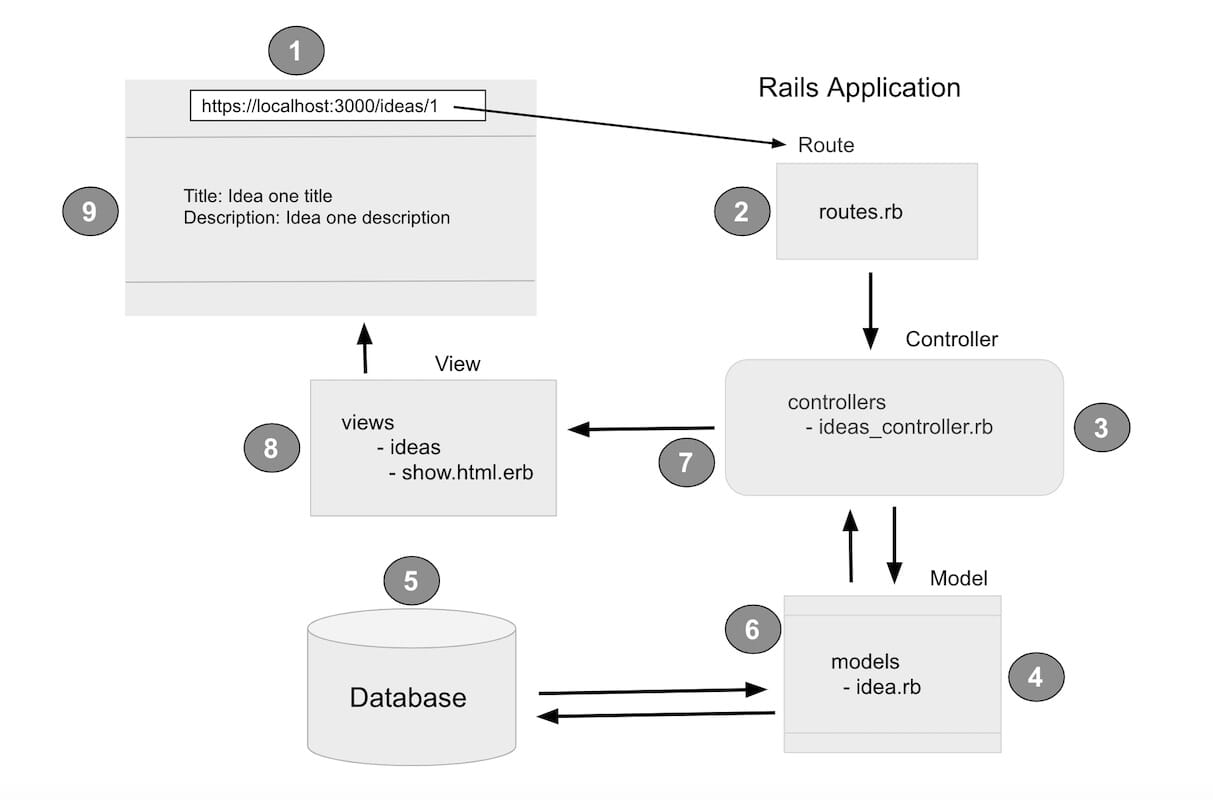
Following image should help you understand how a request from browser goes to routes.rb, ideas_controller.rb, fetch first idea from database, process by ideas_controller.rb again, through show.html.erb displayed to the browser.
Routing error
Let’s try typing url https://localhost:3000/ideas/1 in our browser and see what happens.
You will encounter following error and it is expected.
Routing Error
No route matches [GET] "/ideas/1"
...
| I recommend my students to have friendly attitude with errors as they are great source of learning. |
Fixing routing error
Let’s try to understand error here.
It says, No route matches [GET] "/ideas/1". Typically this is a HTTP GET request. In Rails, we can map such route in the routes.rb file as following.
Rails.application.routes.draw do
resources :ideas, only: [:show]
end
NOTE: only: [:show] means to define only route for ideas/:id where id is the id of idea.
| Restart the Rails server (Ctrl + C and rails s) every time you change the 'routes.rb' to reflect the changes. |
After updating the routes.rb file with above lines, the error should be replaced with following different error:
Routing Error
uninitialized constant IdeasController Did you mean? Ideastore
...
That we will fix in the next page.
CRUD and REST
CRUD
CRUD represents following:
- C: Create
- R: Read
- U: Update
- D: Delete
CRUD are the standard four ways through which we can interact with data. These are the basic functions that all models should have.
REST
REST stands for REpresentation State Transfer.
REST is an architectural pattern for defining routes. It is a way of mapping the HTTP verbs like GET, POST, PATCH/PUT or DELETE with the CRUD actions.
In general, CRUD actions are mapped to the following HTTP actions:
| Action | HTTP Verb |
|---|---|
| Create (C) | PUT/POST |
| Read (R) | GET |
| Update (U) | POST/PUT |
| Delete (D) | DELETE |
Resourceful routing
The line resources :ideas provides following different routes which maps to HTTP Verbs (GET/PUT/POST/DELETE/PATCH) and controller actions.
| Rails provides well defined routing mechanism for CRUD which properly map with HTTP verbs. |
| HTTP Verb | Path | Controller#Action | Used for |
|---|---|---|---|
| GET | /ideas |
ideas#index |
display a list of all ideas |
| GET | /ideas/new |
ideas#new |
return an HTML form for creating a new idea |
| POST | /ideas |
ideas#create |
create a new idea |
| GET | /ideas/:id |
ideas#show |
display a specific idea |
| GET | /ideas/:id/edit |
ideas#edit |
return an HTML form for editing a idea |
| PATCH/PUT | /ideas/:id |
ideas#update |
update a specific idea |
| DELETE | /ideas/:id |
ideas#destroy |
delete a specific idea |
See Resourceful routing from Ruby on Rails Guides to understand more.
Route helpers
Creating a resourceful route will also expose a number of helpers to the controllers or views in your application.
In our case resources :ideas has given us following helpers:
| Helper | URL |
|---|---|
ideas_path |
/ideas |
new_idea_path |
/ideas/new |
edit_idea_path(:id) |
/ideas/:id/edit |
idea_path(:id) |
/ideas/:id |
Checking available routes
Rails provide a handy command to check the available routes in your application. Type following to see yourself:
$ rails routes | grep idea
idea GET /ideas/:id(.:format) ideas#show
NOTE: rails routes will list all the routes available in the app.